For those of you who are just starting to get interested in the world of technology and electronic projects, you might have been confused by the differences between Arduino, ESP, and Raspberry Pi. These three boards are often mentioned in the maker community as popular microcontrollers for beginners. But don’t worry, the following explanation will outline the use of each in technology projects, key features, and their price range in rupiah, explained in a relaxed style as if talking to a peer. Let’s discuss!
Arduino, Beginner-Friendly Microcontroller
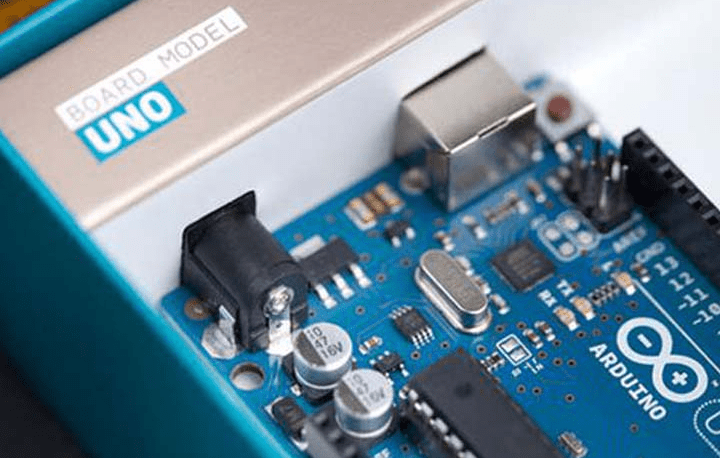
What is Arduino? Arduino is a simple and easy-to-use open-source microcontroller board. It is designed to run one task at a time (it does not use an operating system like a computer). Imagine Arduino as a simple electronic brain that is good at performing one specific job, such as reading sensors and turning on LEDs, repeatedly without getting tired. Arduino programming usually uses the C/C++ language, which has been simplified in the Arduino IDE software, so beginners can quickly understand it. Another advantage is that Arduino has many analog and digital I/O (input/output) pins for connecting various sensors, motors, lights, and other components. Examples of projects often made using Arduino include distance sensor alarms, line follower robots, or simple digital thermometers.
Price & Community: Good news for students’ wallets, the price of Arduino is relatively affordable. The original Arduino Uno version is usually priced around Rp300 thousand, but there are also many clone versions whose prices can be only Rp50–80 thousand in marketplaces. In general, Arduino is indeed cheaper than Raspberry Pi. Furthermore, the Arduino community is very broad and supportive. So if you get stuck, there are many tutorials and forums where you can ask questions. It’s perfect for beginners, right?
ESP32, Low-Budget IoT Champion

What is ESP? The ESP referred to here is mainly the ESP32 (there is also the older ESP8266). The ESP32 is actually similar to Arduino because it is a microcontroller, but with the added feature of built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Imagine you want a project to control home lights via a smartphone or send sensor data to the internet (Internet of Things, or IoT); well, the ESP32 is the champion there. Interestingly, the ESP32 can also be programmed using Arduino code, so those who have tried Arduino will find it easy to switch to ESP. In terms of capability, the ESP32 has a faster 32-bit dual-core processor than the Arduino Uno, plus larger memory, so it can handle somewhat complex IoT tasks. This board fills the gap between Arduino and Raspberry Pi – meaning, if you need a microcontroller that is smarter than Arduino (e.g., needs an internet connection) but not as heavy as a Raspberry Pi, the ESP32 is the perfect choice.
Price & Advantages: In terms of price, the ESP32 is super cheap. In the market, the ESP32 module can be obtained for only tens of thousands of rupiah. There is also the ESP8266 variant which is even cheaper if you only need basic Wi-Fi. For that cost, you already get a microcontroller that has Wi-Fi/Bluetooth – something that usually requires an extra module on a standard Arduino. Crazy, right? That’s why the ESP32 is often dubbed the low-budget IoT champion. Many smart home projects, remote monitoring, and even robots controlled via the internet are made using this board. The ESP user community is also growing rapidly, especially because it is compatible with the Arduino ecosystem, so references and libraries are abundant.
Raspberry Pi, Multi-function Mini Computer
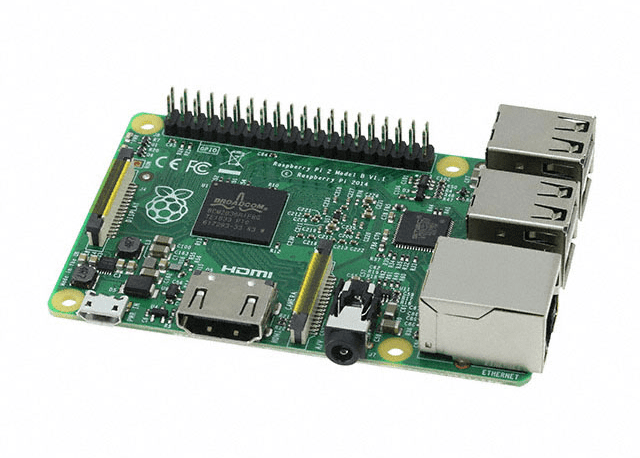
What is Raspberry Pi? Unlike Arduino and ESP, Raspberry Pi is a Single Board Computer (SBC). Simply put, it is a credit card-sized mini computer that already has a processor, RAM, and can run an operating system just like a PC. If Arduino is a smart calculator, Raspberry Pi is like a mini desktop computer. You can plug in a mouse, keyboard, connect to a monitor, and run an OS (generally Raspberry Pi OS based on Linux) to perform various tasks. Raspberry Pi is equipped with computer features such as HDMI output (for display), USB ports (connecting flash drives, cameras, etc.), audio jack, Ethernet, built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. With these specifications, the Pi is capable of performing more complex and multitasking jobs – for example, becoming a small web server, media player, processing camera images, or even running simple artificial intelligence programs.
Advantages & Price: In terms of performance, Raspberry Pi is clearly on a higher level. Its processor speed can reach 1.2–1.6 GHz, which is said to be about 100 times faster than the Arduino 16 MHz clock in some cases. However, this extra capability makes the Raspberry Pi more expensive than regular microcontroller boards. In Indonesia, standard Raspberry Pi models (e.g., Pi 3 or Pi 4 with smaller RAM) are generally sold between Rp500 thousand to Rp900 thousand depending on the version and specifications. Even the latest variants with large RAM can exceed 1 million rupiah (example: Raspberry Pi 4 8GB RAM around 1.1 million). Therefore, for simple projects, using a Pi is not worth it because the cost and power consumption of the Pi are also greater. Raspberry Pi is more suitable if you really need a multitasking mini computer – for example, creating an IoT server, a monitoring system with a camera, or a project that requires a GUI (graphical interface) on the screen. Although more complex, many students and makers learn many new things from Raspberry Pi, ranging from Linux, Python (its main programming language), to networking. Its community is also very broad, so there is always online help if you encounter difficulties.
So, Which one is more suitable?
After reading the explanation above, we can conclude that each has its own uniqueness and use. Arduino is suitable for beginners who want to quickly learn the basics of electronics and programming. This board is perfect for simple projects that do not require many resources or internet connectivity, and have a limited budget. ESP32 (ESP) is the right choice if you want to enter the world of IoT or need Wi-Fi/Bluetooth features in your project, without having to spend a lot of money. Meanwhile, Raspberry Pi is more suitable for more complex projects or those requiring computer-like capabilities – for example, running multiple processes simultaneously, using a camera, or processing large data.
As a quick overview: “For beginners, Arduino is the best starting place; Raspberry Pi offers advanced capabilities but can empty your wallet, and ESP32 provides smart IoT solutions without breaking the bank.” Of course, the final choice depends on your project needs. What is clear is that whatever the choice, the world of technology and electronics is really exciting to explore. If you want to learn more deeply about similar topics and develop expertise in this field, let’s join the Informatics Study Program Telkom University. There, you can learn directly and hone your skills in creating cool projects with Arduino, ESP, Raspberry Pi, and other technologies. Happy creating and hope this is useful!

