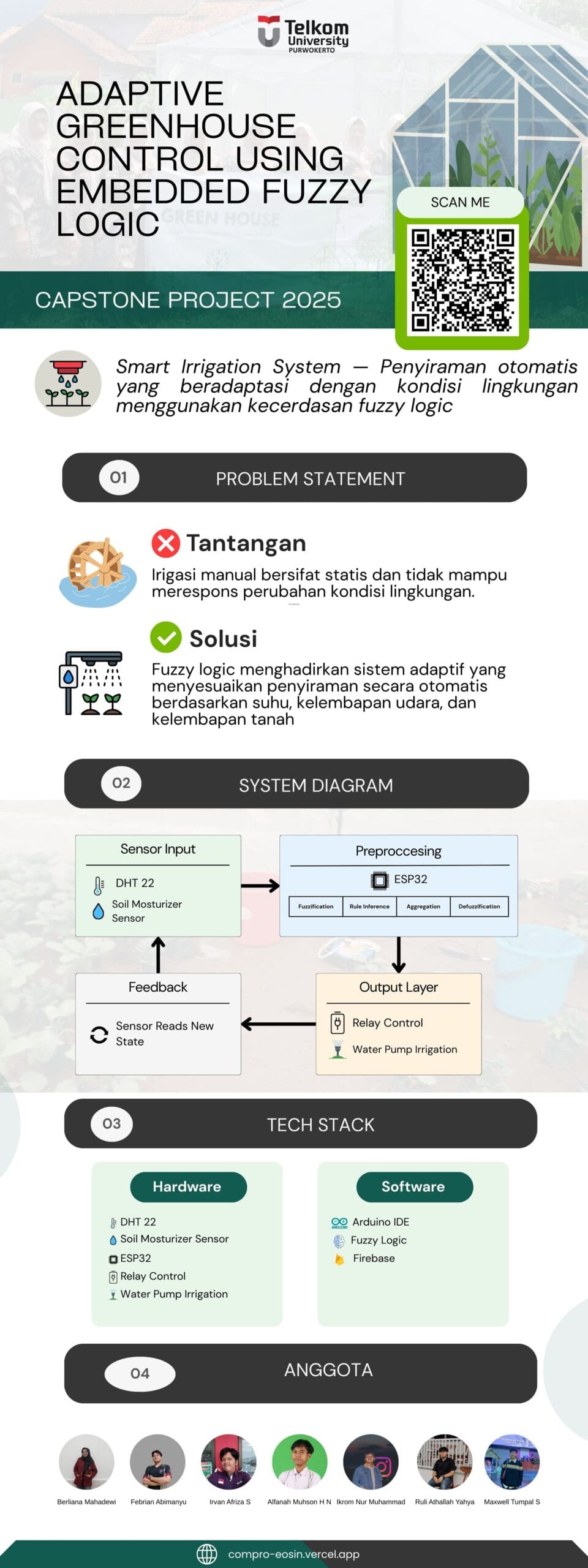
Project Overview
This project aims to develop an automatic irrigation system that uses fuzzy logic to adjust plant watering according to environmental conditions, such as air temperature, soil moisture, and air humidity. This system is designed to overcome the problems of manual irrigation, which is inefficient and unresponsive to changes in environmental conditions.
Problems Encountered
Manual irrigation often cannot respond quickly to changes in environmental conditions, which can result in excessive water usage or insufficient water for plants, affecting plant growth.
Solution Provided
This system uses fuzzy logic to create adaptive irrigation, which is a system that can adjust water flow based on data from temperature and soil moisture sensors. With this technology, irrigation can run automatically and more efficiently, ensuring plants receive sufficient water without waste.
System Diagram
This system consists of several parts:
- Input Sensors: DHT 22 sensor to measure air temperature and humidity, as well as a soil moisture sensor.
- Processing: Data from the sensors is processed using ESP32, which implements the fuzzy logic algorithm.
- Output Control: Based on the data processing results, the system regulates a relay to operate the water pump.
Components Used
Hardware:
- DHT 22 (air temperature and humidity sensor)
- Soil Moisturizer Sensor (soil moisture sensor)
- ESP32 (microcontroller for processing data and controlling the system)
- Relay Control (for controlling the water pump)
- Water Pump Irrigation (automatic irrigation system)
Software:
- Arduino IDE (hardware development platform)
- Fuzzy Logic (algorithm for data processing)
This project was developed by students from class S1IF-10-05, Bachelor of Informatics, Telkom University Purwokerto, namely Berlan Mahadewi, Febrian Abimanyu, Ivan Artiza S, Alfian Muhson H N, Ikrom Nur Muhammad, Rudi Afthalah Yahya, Maxwel Tumpal S.

